Muscle Relaxer
Muscle Relaxer
When people suffer from acute physical pain that persists for an extended period, they are recommended to take a muscle relaxer. It is a drug that affects the functioning of the skeletal muscle and decreases muscle tension. Muscle relaxers are helpful for the treatment of acute pain caused due to muscle tension and spasms.
Muscle spasms are familiar as muscle cramps. It occurs when the muscle involuntarily and forcibly contracts, which cannot be controlled and relaxed. According to practicalpainmanagement [1], muscle spasms involve sudden and involuntary muscle contraction. It results in muscle twitching and jerking, causing back and neck pains. Muscle tension occurs when the muscles remain semi-contracted for a certain period. They usually occur due to physiological effects of stress, leading to severe back pain.
Types of Muscle relaxers
We can divide muscle relaxers into two categories- antispasmodics and neuromuscular blockers.
- Antispasmodics, described by medicalnewstoday [2], is the type of muscle relaxer that works on the spinal cord. It ensures to improve musculoskeletal pain and muscle spasms.
- Neuromuscular blockers [3] work on the nervous system by blocking the neural transmission from reaching the central nervous system.
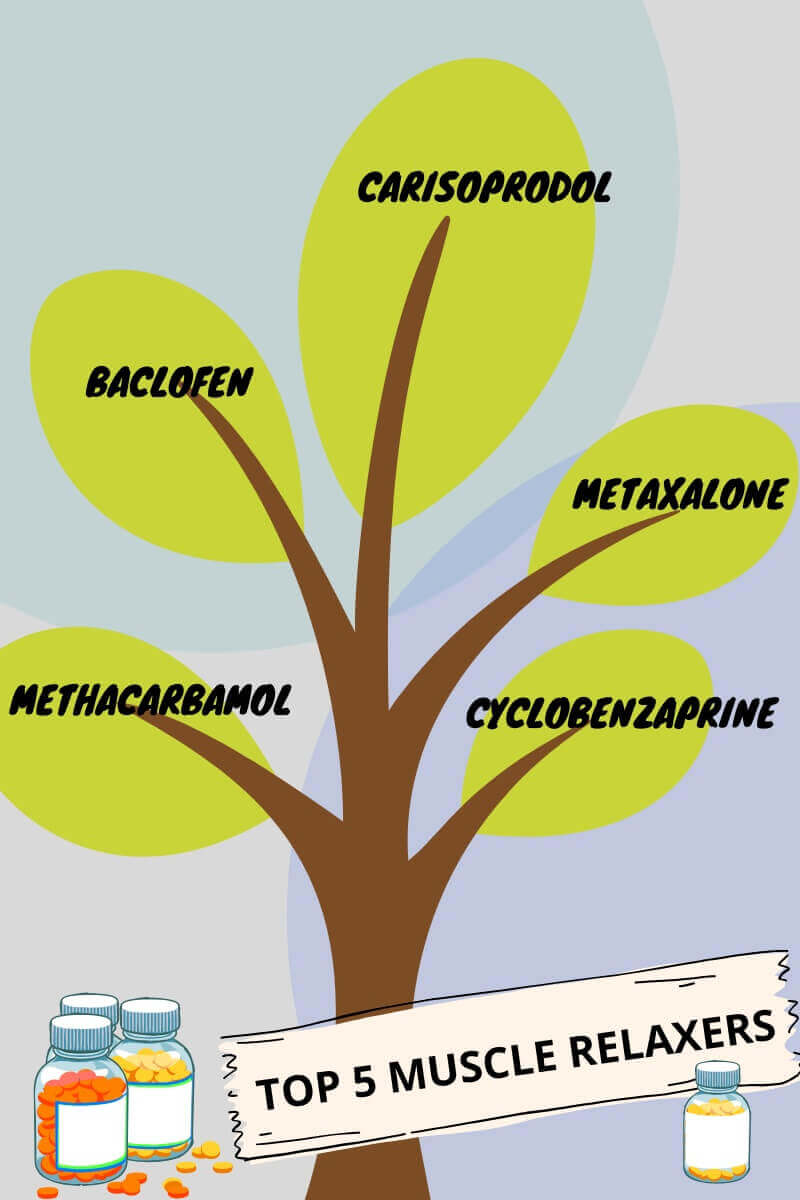
What are the top 5 muscle relaxers?
There are various muscle relaxers available commercially. However, the five best muscle relaxers are Carisoprodol, Baclofen, Metaxalone, Cyclobenzaprine, and Methocarbamol.
Can one buy muscle relaxants over the counter?
No, the Soma pill (including all other muscle relaxers) are prescription analgesic and is not available over the counter. Now, with buysoma online pharmacy, it is possible to order Soma online without a prescription; however, such users should strictly follow the administrative guidelines of the pain medication.
When should one buy muscle relaxers?
This group of drugs can treat pains from cuts, burns, toothaches, post-surgical pain, and labor pain during childbirth. A research article by Pubmed [4] also indicates the efficacy of muscle relaxers for helping with pain associated with cerebral Palsy.
How do they function in the body?
Muscle relaxers mainly differ from other analgesics in their chemical structures or composition. However, all muscle relaxers act as depressants of the central nervous system, which causes a sedative effect. It prevents the nerves from sending a neural transmission to the brain.
The on-set action of these medications is rapid, and their effect typically lasts for 4-6 hours. They are mainly available for oral consumption, which one should use for a short period of 2-3 weeks. People who belong to the age group of 17 to 65 years can take muscle relaxers.

What is the best and the strongest muscle relaxer?
Carisoprodol is the strongest muscle relaxer drug available under the brand name Soma. Carisoprodol got approval for medical use in the United States in 1959.
Soma pill is available in two dosages. Beginners should start with a lower dose. Users can buy Soma 350mg after consulting a physician. Gradually the strength of the muscle relaxer can be increased based on the severity of pain. However, one must not take higher dosages of Soma pills without a valid medical prescription to prevent side effects.
Is a muscle relaxer a pain killer?
The primary use of a muscle relaxer is to work directly on the muscles by helping with muscle spasms and making the muscles less tense. It will, in turn, reduce pain and physical discomfort.
Pain killers relieve pain not explicitly related to muscles like cuts and burn injuries.
Are muscle relaxers safe?
Yes, muscle relaxants are safe to take. Medical experts recommend muscle relaxers to treat acute and stubborn muscle pain. Though it is safe, people taking higher dosages of Soma must not overdose on the medication. One must only order Soma 500mg online under the guidance of a medical professional. Improper administration of muscle relaxers such as the Soma pill can cause addiction.
A paper published by NCBI [5] showcases patients experiencing blurry vision, headache, and dependency from using muscle relaxers. Some common side effects of muscle relaxers, according to the website americanaddictioncenters [6], are mentioned below:
- Drowsiness
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Agitation
- Irritability
- Dry mouth
- Decreased blood pressure
Although the signs of adverse effects of the Soma pill are mild, under certain conditions, it can cause severe health issues, such as-
- Sedation is one common adverse effect of muscle relaxers. Thus one should not drive a vehicle or operate heavy machinery after taking the analgesic.
- Overdose and a combination of muscle relaxers and other addictive substances can cause fatal effects.
- People with an allergy might suffer from hives, breathing problems, and swelling of the chest.
Are muscle relaxers safe during pregnancy and breastfeeding?
A pregnant and breastfeeding mother should be cautious, and most importantly, she should take muscle relaxers only under the strict recommendation of a gynecologist. However, as per reports by spine-health [7], Cyclobenzaprine is a muscle relaxer rated B by the FDA and is considered safe during pregnancy.

Summary
In conclusion, Muscle relaxers are pain relief drugs that can treat acute pain due to muscle spasms. Always follow preventive measures while taking a muscle relaxer, as it can help you avoid the pain medication’s adverse effects. Above all, remember that muscle relaxers are not the cure for your muscle pain.
Reference-
The information given on this page is collected through in-depth and meticulous research and we would like to give credit to all the websites and publishers from where the pieces of information were collected-
- Jeffrey Fudin, et.al (2017); “A Review of Skeletal Muscle Relaxants for Pain Management”, practicalpainmanagement.
- Jessica Caporuscio (2021); “Which muscle relaxers are available?”, Medicalnewstoday.
- Wikipedia; “Neuromuscular-blocking drug”.
- Jacki Peck, et.al (2020); “Oral Muscle Relaxants for the Treatment of Chronic Pain Associated with Cerebral Palsy”, Pubmed.ncbi.
- Corey Witenko, et.al (2014); “Considerations for the Appropriate Use of Skeletal Muscle Relaxants for the Management of Acute Low Back Pain”, Ncbi.nml.
- Micheal Kaliszewski (2021), “Side effects of Muscle relaxers”, Americanaddictioncenters.
- Kathee de Falla (2019), “Muscle Relaxants: List of Common Muscle Relaxers”, Spine-Health.
Showing the single result
Showing the single result